The latest national census data has been released, offering a fresh perspective on the demographic and economic landscape of the United States. In this update, Arizona and its capital city, Phoenix, reveal significant trends that underscore their growing influence on the national stage. From population shifts to income levels and business growth, The Business Journals takes an in-depth look at how these key players stand up in comparison to other regions across the country. This analysis provides valuable insight into the opportunities and challenges facing Arizona as it positions itself for the future.
Arizona and Phoenix Population Trends Reveal Economic Shifts
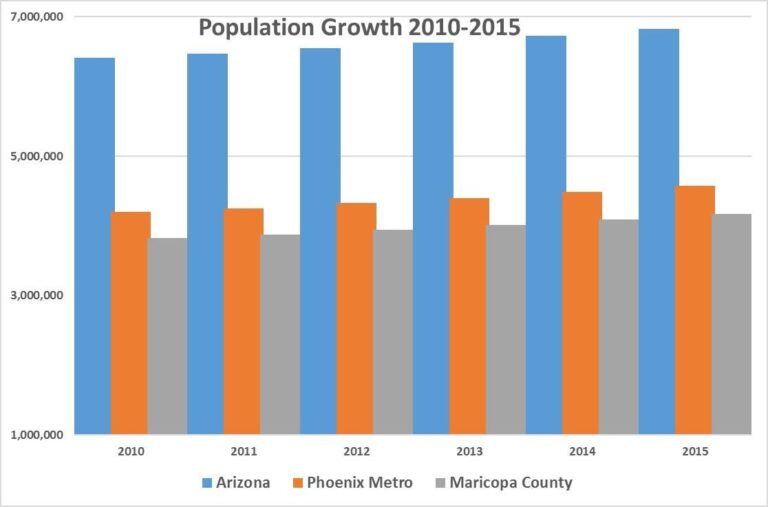
The latest census data uncovers a remarkable population surge in Arizona, particularly concentrated in Phoenix, signaling profound economic transitions. The influx of new residents is fueled not just by retirees, but increasingly by young professionals and families drawn by expanding job prospects in tech, healthcare, and renewable energy sectors. This demographic diversification is reshaping the economic landscape, amplifying demand for housing, infrastructure, and services in urban and suburban locales alike.
Key population growth factors include:
- Tech industry expansion: Phoenix emerges as a competitive tech hub attracting startups and established companies.
- Affordable living costs: Relative affordability compared to coastal metros continues to pull migration eastward.
- Strategic location: Proximity to major markets makes Phoenix a logistics and distribution focal point.
| Year | Arizona Population (millions) | Phoenix Population (millions) | Unemployment Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2010 | 6.39 | 1.44 | 9.5 |
| 2020 | 7.28 | 1.61 | 7.2 |
| 2023 (est.) | 7.55 | 1.69 | 5.4 |
Impact of New Census Data on Local Housing and Infrastructure
The latest census figures reveal significant shifts that are reshaping Phoenix and the broader Arizona landscape, forcing policymakers to reconsider housing and infrastructure strategies. Rapid population growth, particularly in suburban and previously underdeveloped areas, is intensifying the demand for affordable housing, while existing communities face heightened pressure on roadways, public transit, and utilities. Key stakeholders highlight that to accommodate this surge, a multi-pronged approach focusing on sustainable development, zoning reform, and investment in public amenities is no longer optional but essential.
Among the critical challenges emerging from the new data are:
- Housing shortages: A mismatch between supply and growing demand leads to rising rental costs and home prices.
- Infrastructure strain: Aging transport networks require upgrades to manage increased commuter volumes efficiently.
- Resource allocation: Water and energy systems must evolve to support expanding neighborhoods without compromising existing residents.
| Category | 2010 Census | 2020 Census | % Change |
|---|---|---|---|
| Population | 6.4 million | 7.2 million | 12.5% |
| Housing Units | 2.5 million | 2.8 million | 12.0% |
| Public Transit Ridership | 45 million | 52 million | 15.6% |
Key Demographic Changes Shaping Workforce and Business Growth
Arizona, particularly Phoenix, is experiencing a notable demographic shift that is reshaping its workforce landscape. The new census data reveals a surge in younger professionals migrating into the region, drawn by burgeoning tech hubs and expanding healthcare industries. This inflow has contributed to a more diverse labor pool with heightened cultural and educational backgrounds, which businesses are leveraging to drive innovation. Simultaneously, the aging population is gradually increasing, urging companies to refine workforce strategies to include retention and reskilling programs tailored for older employees.
Key demographic trends impacting Arizona’s business environment include:
- Rising Hispanic population, now accounting for over 30% of the workforce.
- Growth in dual-income households enhancing local economic stability.
- Increase in remote workers enabling businesses to tap into broader talent pools.
| Demographic Indicator | 2010 | 2020 | Change % |
|---|---|---|---|
| Population under 35 | 45% | 52% | +7% |
| Hispanic workforce | 25% | 31% | +6% |
| Remote workers | 8% | 22% | +14% |
Strategic Recommendations for Policymakers and Investors in Arizona
To capitalize on Arizona’s evolving demographic landscape, policymakers should prioritize investments in infrastructure and affordable housing to accommodate the rapid population growth, particularly in urban centers like Phoenix. Enhancing public transportation systems and expanding access to quality education will promote sustainable urban development and attract skilled professionals. Initiatives aimed at fostering innovation hubs through public-private partnerships could further bolster economic diversification, positioning Arizona as a competitive state for technology and renewable energy sectors.
Investors must leverage emerging opportunities by focusing on sectors aligned with demographic trends such as healthcare, real estate, and green technologies. Prioritizing developments in suburban areas that are witnessing population influxes can yield substantial returns, especially when coupled with sustainable building practices. Consider the table below highlighting key growth areas and recommended investment focuses:
| Growth Area | Investment Focus | Potential Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Phoenix Metro | Residential & Transit | Increased housing availability, reduced congestion |
| Tech Corridors | Innovation Hubs & Startups | Job creation, economic diversification |
| Suburban Zones | Healthcare Facilities | Improved services, attract families |
| Renewable Energy Sites | Clean Tech Infrastructure | Environmental sustainability, energy resilience |
In Summary
As the latest national census data unfolds, Arizona and Phoenix demonstrate significant shifts that reflect broader demographic and economic trends. These insights not only highlight growth patterns but also underscore emerging challenges and opportunities for businesses, policymakers, and residents alike. Moving forward, stakeholders will be closely watching how these developments shape the region’s future trajectory within the national landscape.